
There are wrapper scripts in `/usr/bin` to run these, but running them as modules without using the wrapper script is strongly recommended. The Python modules `pip` and `venv` for installing modules and working with Python virtual environments are installed. You can also use `python3.6` as the command to specifically run Python 3.6. For an explanation of the above command, see Working with AppStreams below. This causes the `python36-devel` package to be installed that are needed to build any Python module that use dynamically loaded code such as C/C++. For development, use the `build` profile. Python36 3.6 build, default Python programming language, version 3.6įor the `python36` module, there are two profiles: `default` and `build`. Python27 2.7 default Python programming language, version 2.7 Wait for the installation to complete.First, see what Python modules are available as part of the Application Stream Repository: To add the IUS repository, use the command: sudo yum install $(rpm -E '%').rpm If you are using a CentOS release older than 7.7, you need to add IUS, a yum repository that provides newer software versions and includes Python 3. If you have CentOS version 7.7 or newer, skip to the next step. Before you move on to installing Python 3 on your CentOS system, make sure it is available in the package repository. Start by updating the repository: sudo yum update -yĢ. If you prefer installing version 3.6.8, follow the steps listed below.ġ. For instructions on how to do so, refer to the next section. For the latest major release, you need to install the package from the source code.
The newest Python 3 version available in the package manager is Python 3.6.8. Option 1: Install Python From Package Manager
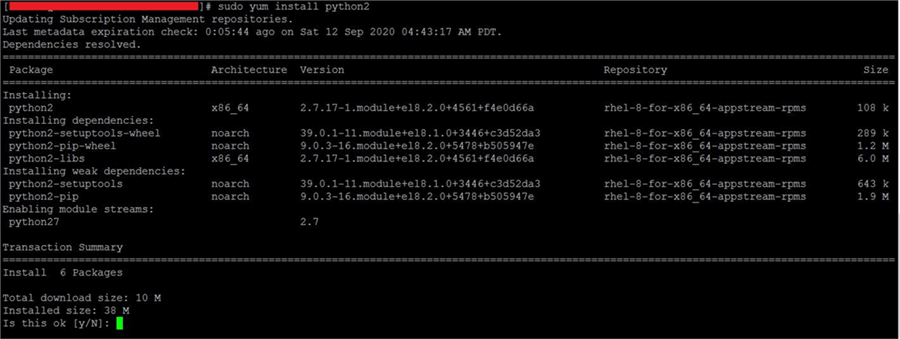

There are two ways to install Python 3 on your CentOS system: A terminal window/command line (Ctrl-Alt-F2).The yum package manager, included by default.Access to a user account with sudo privileges.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
